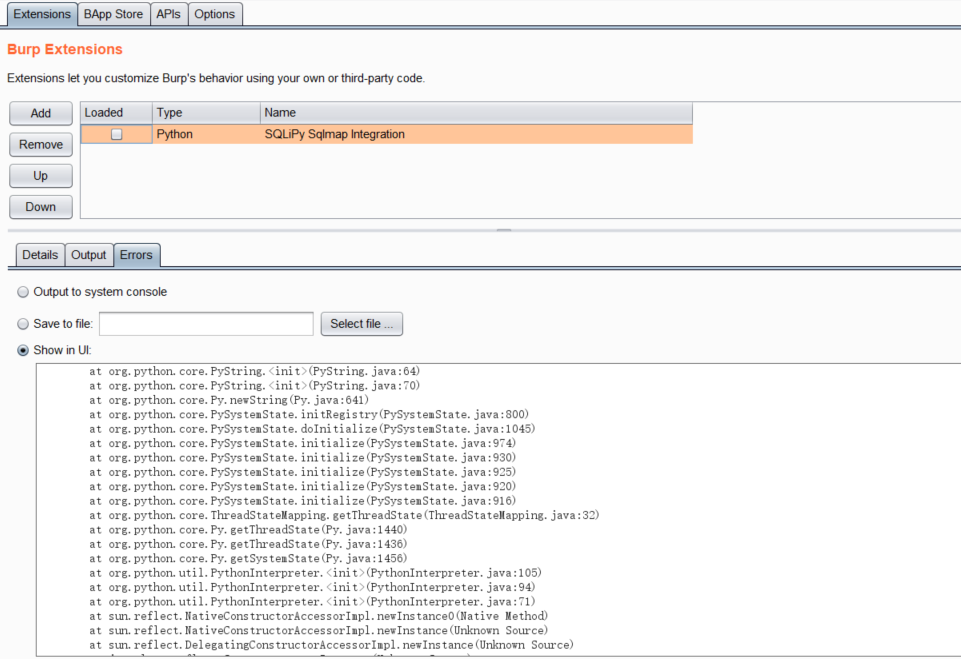
原理是遍历所有节点,除了已经到最后目标不遍历外,其它都遍历。
package com.boeyu.matrixlib;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class PathAirthmetic {
private int width; //矩阵宽
private int height; //矩阵高
private Pos mStartPos; //起点坐标
private Pos mEndPos; //终点坐标
private int[][] mMatrix;
private List<List<Pos>> mPathList = new ArrayList<>(); //最终成功路径
/**
* 开始计算
*
* @param matrix 二维矩阵数组,0代表可通行,1不可通行
* @param startX 开始坐标x
* @param startY 开始坐标y
* @param endX 结束坐标x
* @param endY 结束坐标y
* @return
*/
public List<Pos> start(int[][] matrix, int startX, int startY, int endX, int endY) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return null;
}
width = matrix[0].length;
height = matrix.length;
System.out.println("width=" + width + ",height=" + height);
mMatrix = matrix;
mStartPos = new Pos(startX, startY);
mEndPos = new Pos(endX, endY);
mPathList.clear();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Pos> posList = new ArrayList<>();
posList.add(mStartPos);
boolean success = enumNextPos(posList, startX, startY);
System.out.println("time=" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
if (mPathList.size() > 0) {
System.out.println("path=" + mPathList.size());
List<Pos> minPath = mPathList.get(0);
for (List<Pos> poses : mPathList) {
//System.out.println(poses.toString());
if (poses.size() < minPath.size()) {
minPath = poses;
}
}
return minPath;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 开始计算
*
* @param matrix 一维矩阵数组
* @param width 矩阵列数
* @param startX 开始坐标x
* @param startY 开始坐标y
* @param endX 结束坐标x
* @param endY 结束坐标y
* @return
*/
public List<Pos> start(int[] matrix, int width, int startX, int startY, int endX, int endY) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int[][] mMatrix = new int[matrix.length / width][width];
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int x = i % width;
int y = i / width;
mMatrix[y][x] = matrix[i];
}
return start(mMatrix, startX, startY, endX, endY);
}
/**
* 遍历下一个节点
*
* @param path
* @param x
* @param y
* @return
*/
private boolean enumNextPos(List<Pos> path, int x, int y) {
mMatrix[y][x] = 1;
List<Pos> subPos = new ArrayList<>();
if (x - 1 >= 0 && mMatrix[y][x - 1] == 0) {
subPos.add(new Pos(x - 1, y));
}
if (x + 1 < width && mMatrix[y][x + 1] == 0) {
subPos.add(new Pos(x + 1, y));
}
if (y - 1 >= 0 && mMatrix[y - 1][x] == 0) {
subPos.add(new Pos(x, y - 1));
}
if (y + 1 < height && mMatrix[y + 1][x] == 0) {
subPos.add(new Pos(x, y + 1));
}
boolean success = false;
for (Pos pos : subPos) {
if (isEquals(pos.x, pos.y, mEndPos.x, mEndPos.y)) {
List<Pos> mList = new ArrayList<>(path);
mList.add(pos);
mMatrix[pos.y][pos.x] = 0;
mPathList.add(mList);
return true;
}
List<Pos> mList = new ArrayList<>(path);
mList.add(pos);
success |= enumNextPos(mList, pos.x, pos.y);
mMatrix[pos.y][pos.x] = 0;
}
return success;
}
private boolean isEquals(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
return x1 == x2 && y1 == y2;
}
public static class Pos {
int x;
int y;
public Pos(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "(" + x + "," + y + ")";
}
}
}
package com.boeyu.matrixlib;
import java.util.List;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//从左上角行走至右下角
//************ 二维矩阵演示 ****************
List<PathAirthmetic.Pos> posList = new PathAirthmetic().start(new int[][]{
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}
}, 0, 0, 7, 3);
if (posList != null) {
System.out.println("min path:" + posList.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("fail");
}
//************ 一维矩阵演示 ****************
List<PathAirthmetic.Pos> posList2 = new PathAirthmetic().start(new int[]{
0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0
}, 8, 0, 0, 7, 7);
if (posList2 != null) {
System.out.println("min path:" + posList2.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("fail");
}
}
}